
The packaging business, which depends on plastics for their affordability, durability, and light weight, imports plastic materials. Plastic packaging is commonly utilized for food, drinks, medications, and other consumer products. A wide range of products fall under this category, including finished goods, packaging products, construction articles, raw plastic materials (polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC), and plastic products.
India is import-dependent for over 55% of PVC. India also imports higher quantity of other polymers such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polycarbonate, and polyamide, among others to meet its requirement.
News: As per media sources, during the January-March 2022 quarter, India's import of plastics products continued with an estimated value of Rs 6842 crore. Annualising the growth, India’s import of plastic products could have grown 60% to Rs 27370 crore for CY22, post a 52% rise in imports in CY21.
Views: India is import-dependent for over 55% of PVC. India also imports higher quantity of other polymers such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polycarbonate, and polyamide, among others to meet its requirement. Raw materials are costlier in India compared to the competing countries. Input cost is at least 10-15% higher than that in China and South East Asian countries. Also, India has granted concessions to Vietnam and Thailand under Free Trade Agreement (FTA), which allows these countries to dispatch more products to India.
India’s increasing reliance on plastic imports with a sharp rise this year urged CATR to decipher this dependence and look for ways to balance the situation. With the right policies in place, the industry has the potential to decrease the negative trade balance and increase its global footprint.

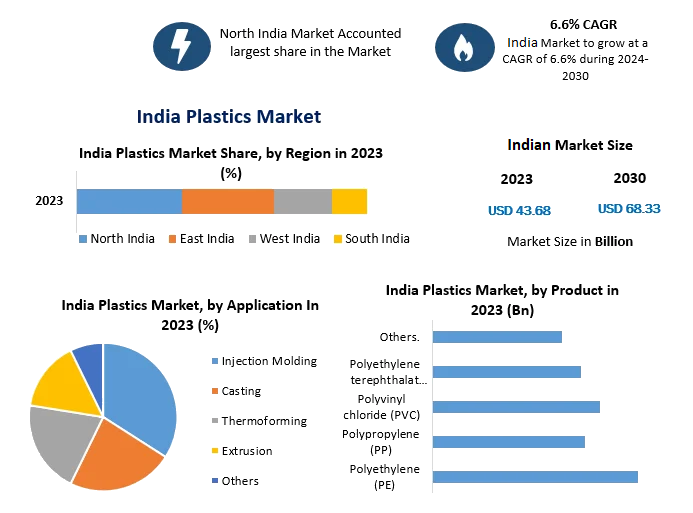
Plastics have been playing a predominant role in shaping our lives. 100 years young in comparison to traditional materials, plastic has accounted for a global production of 367 MT in 2021. Being the third largest consumer of plastics, India’s share of global plastic use is 6.4%and stats reveal a projection of 160.4 million tons use in India by 2060 from an estimated demand of 15 million tons in 2021-22.
The Indian plastic industry has made significant achievements since its inception with the production of polystyrene in 1957. By catering to an entire spectrum of daily use items of life since ages, per capita consumption of plastics in India is estimated at 15 kg in 2021, from 13.6 kg in 2018.